Services
Thyroid Disease
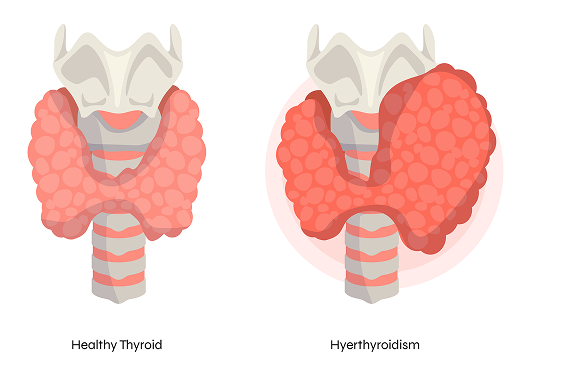
Thyroid Disease
The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped gland that located in the front of the lower part of neck. The thyroid is an endocrine gland that secretes thyroid hormones which circulate in blood to control various functions of our body. There are two types of thyroid hormones: T4 and T3 which control the metabolism of the body.
Patients suffering from enlarged thyroid gland, thyroid nodules and thyroid cancer have to undergo surgery for various indications. A large group of population also suffers from hypothyroidism needs regular medical management and close monitoring to prevent acute and long term complications. We provide an end to end solution for all range of thyroid problems.
Common problems of thyroid gland
The thyroid gland produces hormones that affect your body’s metabolism and energy level. Thyroid problems are among the most common medical conditions but, because their symptoms often
Hypothyroidism (Underactive thyroid)
The most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto’s thyroiditis leading to underactive gland. In this condition, the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland.
Common symptoms of hypothyroidism are:
- Fatigue or lack of energy
- Weight gain
- Feeling cold
- Dry skin and hair
- Heavy menstrual periods
- Constipation
- Slowed thinking
Diagnosis
Patients with hypothyroidism have an elevated level of serum TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone).
Treatment
Thyroid hormone in pill form on a daily basis usually for life time.
Surgical Aspect
Lymphocytic thyroiditis may be associated with thyroid lymphoma with perplexing cytology and clinical picture and need regular clinical follow up and high index of suspicion.
The most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto’s thyroiditis leading to underactive gland. In this condition, the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland.
Common symptoms of hypothyroidism are:
- Fatigue or lack of energy
- Weight gain
- Feeling cold
- Dry skin and hair
- Heavy menstrual periods
- Constipation
- Slowed thinking
Diagnosis
Patients with hypothyroidism have an elevated level of serum TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone).
Treatment
Thyroid hormone in pill form on a daily basis usually for life time.
Surgical Aspect
Lymphocytic thyroiditis may be associated with thyroid lymphoma with perplexing cytology and clinical picture and need regular clinical follow up and high index of suspicion.
Hypothyroidism (Overactive thyroid)
The most common cause of hyperthyroidism is Graves’ disease and toxic nodular goiter. This occurs when the body’s immune system over stimulates the thyroid or due to over secreting thyroid nodule. Grave’s disease sometimes gets better during pregnancy and may flare up post delivery.
Common symptoms of hyperthyroidism are:
- Jitteriness, shaking, increased nervousness, irritability
- Rapid heartbeat or palpitations
- Increased sweating
- Weight loss
- Fatigue, feeling exhausted
- More frequent bowel movements
- Shorter or lighter menstrual periods
- Enlargement of eyes with bulging and redness
Medications can also be used for treatment. These drugs slow down the working of thyroid and restore normal levels. However, they usually need to be taken for 6-12 months and 60-80% of patients have a relapse when they stop taking them. These drugs are associated with serious side effects in a small percentage of patients taking them. Surgical removal of the complete thyroid (total thyroidectomy) is treatment of choice but needs specialist thyroid surgeon for optimal safety and results. Consultation with a thyroid specialist (Endocrine Surgeon) is highly recommended to determine which treatment is best for you!
Thyroid nodules (Lumps) / Goiter & Thyroid Cancers
Goiter (enlarged thyroid)
A goiter simply refers to increase in size of the thyroid gland. A goiter can become large sized before it causes symptoms of compression, like difficulty breathing or swallowing or change in the voice. A goiter may be associated with hormonal imbalance; it may contain one or several nodules that can be cancerous in some cases. The evaluation of goiter will require some blood test, thyroid ultrasound, CT scan, thyroid scan etc. If there is doubt of thyroid cancer or pressure changes, then surgery to remove all or part of the goiter might be warranted. If the entire thyroid is removed, the patient will require lifelong thyroid hormone replacement.
Thyroid nodule
Thyroid nodule is thyroid enlargement as single or multiple discrete nodules. Thyroid nodules or swelling can be benign(non cancerous as well as cancerous. Very large sized nodules will cause compression on wind pipe and will lead to uneasiness in neck and breathing difficulty. It can sometimes also lead to change in voice. They are usually painless. Some times they may be associated with hormonal imbalance. At present, it is unclear why nodules form. Ultrasound, FNAC and thyroid scan are helpful in evaluating these masses. Cold nodules found on thyroid scan have higher chances of becoming cancerous. Surgery is the mainstay of treatment.
Thyroid nodule
Thyroid nodule is thyroid enlargement as single or multiple discrete nodules. Thyroid nodules or swelling can be benign(non cancerous as well as cancerous. Very large sized nodules will cause compression on wind pipe and will lead to uneasiness in neck and breathing difficulty. It can sometimes also lead to change in voice. They are usually painless. Some times they may be associated with hormonal imbalance. At present, it is unclear why nodules form. Ultrasound, FNAC and thyroid scan are helpful in evaluating these masses. Cold nodules found on thyroid scan have higher chances of becoming cancerous. Surgery is the mainstay of treatment.
Thyroid cancers
Thyroid cancer is the one of the commonest cancer of the endocrine glands. They will also present as thyroid nodules (swelling in neck). This may be associated with change in voice, blood in cough, breathing difficulty. Cancer is diagnosed on thyroid biopsy. The different types of thyroid cancer are papillary cancer, follicular cancer, medullary cancer and anaplastic cancer.. Most of the time, thyroid cancer is confined to the neck. In about 10% of cases, it can spread outside the neck to other organs like the lungs or bones. Mainstay of treatment is surgery which involves removing of entire thyroid gland along with lymph nodes followed by radioactive iodine in some cases. They need life long follow up.
Thyroid and pregnancy
Most of the thyroid problems of hormonal imbalance and size enlargement can occur in pregnancy. Abnormal blood reports in pregnancy should be interpreted carefully as they may not be due to a disease state.. Differentiating these findings from a true thyroid abnormality might be challenging and require the expertise of a thyroid specialist. Hormonal treatment during pregnancy needs to be monitored more frequently. Radioactive iodine for investigation and treatment are contraindicated in pregnancy. Post-partum thyroiditis is an inflammatory condition of the thyroid gland which occurs within a few months of delivery and can result in permanent hypothyroidism. Thyroid cancer can occur during pregnancy and might necessitate surgical treatment that should be done preferably in second trimester. Grave’s disease sometimes gets better during pregnancy and may flare up post delivery.
Thyroid Surgery
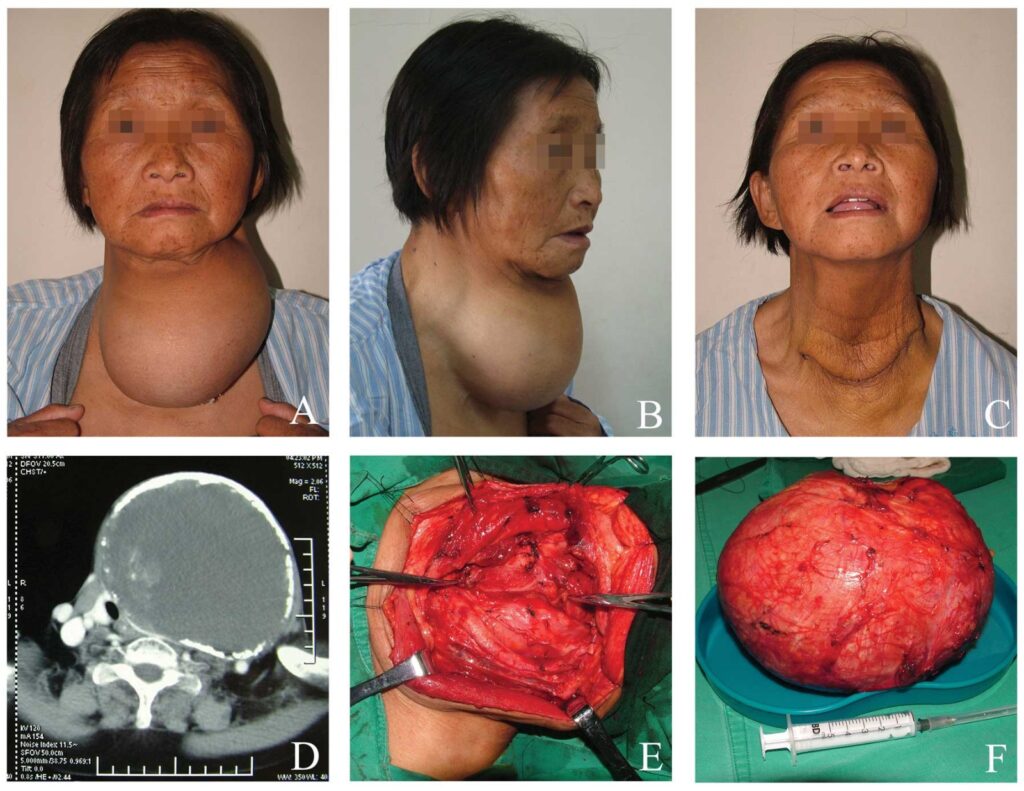
Thyroid surgery is performed for several reasons and can include symptomatic thyroid nodules, recurrent thyroid cysts, goiter, Graves disease, and to rule out or treat thyroid cancer. The purpose of thyroid surgery is to remove part or all of the thyroid gland. You will be in the hospital usually one night. Your surgeon will explain your specific surgery and why it is recommended in your case. As with any surgical procedure, there are risks involved. There is a risk of bleeding, but this is very low. The average blood loss is less than an ounce. The risk of infection is so low that antibiotics are not routinely used. There is also a very low risk of injury to important nerves, called recurrent laryngeal nerves, in the neck. These nerves control the vocal cords. Injury to these nerves could affect your voice. The parathyroid glands are located near the thyroid gland and may become temporarily dysfunctioning after thyroid surgery. This can result in a drop in blood calcium levels. There is also a small risk associated with anesthesia. However, the relative risk of complications is very low and is usually outweighed by the potential benefits of having the surgery. Your surgeon will go over this information with you and answer any questions you might have.
Before surgery
Once the surgery has been scheduled, arrangements will be made for your pre-operative evaluation. You will meet with a nurse practitioner or physician’s assistant from the anesthesiology department. The pre-op exam can include laboratory work, chest x-ray, and EKG.
If you take aspirin or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents you should stop taking these one week before surgery. The night before surgery. do not have anything to eat or drink after midnight. Get a good night’s sleep.
The day of surgery
Your doctor’s secretary will let you know where your surgery will be and what time you need to arrive at the hospital on the day before surgery. During the surgery, your family can wait in the family waiting area. They will be kept updated by the patient representative and operating room staff. The surgeon will speak with them after surgery has been completed.
What will happen in surgery?
You will be given general anesthesia to put you to sleep. You are positioned with special pillows under your neck to tilt your head back. An incision is made at the base of your neck and is about three to four inches long. Using magnifying lenses, the surgeon locates the thyroid gland and associated structures and all or part of the thyroid is removed. In some cases additional surgery will involve removal of lymph nodes and other structures. The incision is stitched closed and is then covered with steri-strip tapes and a dry gauze dressing. The operation generally lasts from two to three hours. After surgery, you will stay in the recovery room for several hours. You will be monitored closely as you recover from the anesthesia.
After surgery
Evening after surgery you will have a liquid diet for dinner. You may have a sore throat. The nurse will provide lozenges and/or throat spray to help relieve this. If you need something for pain, the nurse will give you a liquid pain medicine. You will have a dressing on your neck which will be removed in the morning. The head of your bed will be raised to decrease swelling. You will have an intravenous line to give you fluids until the next day. You will have routine blood tests. You will be offered regular food the next morning. Most people are ready to go home after breakfast.
The Incision
After the dressing is removed, you will notice that the incision is covered with tapes (steri-strips). These will stay on for about a week. The stitches will be absorbable and will not required to be removed. Infection is extremely rare. If you notice any redness or drainage from the incision contact your surgeon. After the stitches are removed, the most important thing you can do to improve the appearance of your scar is to protect it with sunscreen that has a sun protection factor (SPF) of 30 for an entire year. During the year your scar may become raised or red, but will almost always fade into a thin line which will be less noticeable.
How will I feel after surgery?
Everyone behaves differently after surgery different. You will most likely be tired and a bit sore for a few days. You may have pain not only from your incision, but also from muscle soreness in your upper back and shoulders. This is from the positioning in the operating room during the surgery. You will have liquid pain medicine in the hospital and a prescription for pain pills at home.
You may have a sore throat. This is a result of the placement of anesthesia tubes during surgery. Throat lozenges and spray usually help. Your neck may be slightly swollen as well. You may feel like you have a lump in your throat when you swallow. This will improve after a few days but may continue for a week or so. If you notice sudden swelling in your neck contact your surgeon’s office. Your calcium level may drop after surgery. This is related to disturbance of the parathyroid gland, which regulate calcium balance. This will be monitored through blood tests. You may notice numbness and tingling of your fingers or around your mouth. You will have instructions about taking calcium replacement if needed.
Recovering at Home
Most people take1 to 2 days off to recover. You should not drive for at least a week. There are no other restrictions. Depending on the amount of thyroid tissue that was removed and the reason for your surgery, you may be placed on thyroid hormone. Your doctor will discuss your situation with you.
Everyone behaves differently after surgery different. You will most likely be tired and a bit sore for a few days. You may have pain not only from your incision, but also from muscle soreness in your upper back and shoulders. This is from the positioning in the operating room during the surgery. You will have liquid pain medicine in the hospital and a prescription for pain pills at home.
You may have a sore throat. This is a result of the placement of anesthesia tubes during surgery. Throat lozenges and spray usually help. Your neck may be slightly swollen as well. You may feel like you have a lump in your throat when you swallow. This will improve after a few days but may continue for a week or so. If you notice sudden swelling in your neck contact your surgeon’s office. Your calcium level may drop after surgery. This is related to disturbance of the parathyroid gland, which regulate calcium balance. This will be monitored through blood tests. You may notice numbness and tingling of your fingers or around your mouth. You will have instructions about taking calcium replacement if needed.
Recovering at Home
Most people take1 to 2 days off to recover. You should not drive for at least a week. There are no other restrictions. Depending on the amount of thyroid tissue that was removed and the reason for your surgery, you may be placed on thyroid hormone. Your doctor will discuss your situation with you.